About gingival recession (receding gums)
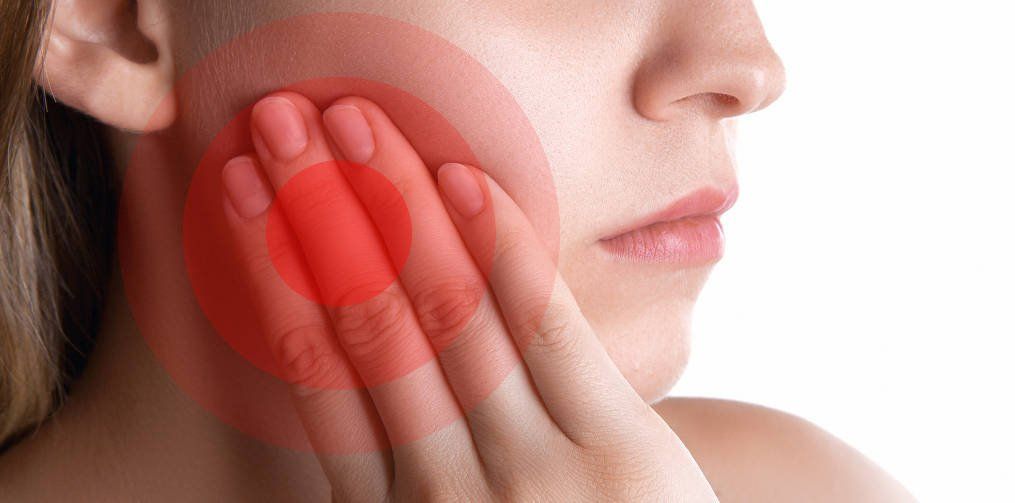
Is a condition also known as receding gums, it consist in the exposure in the root of the teeth caused by a loss of gum tissue and/or retraction of the gingival margin from the crown of the teeth.
When gum recession occurs, appear “pockets,” or gaps, form between the teeth and gum line, making it easy for disease-causing bacteria to build up. If left untreated, the supporting tissue and bone structures of the teeth can be severely damaged, and may ultimately result in tooth loss
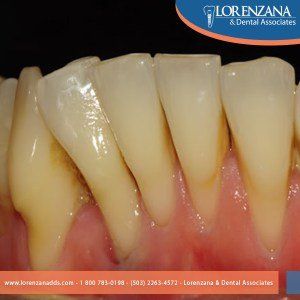
Causes:
- Periodontal diseases: These are bacterial gum infections that destroy gum tissue and supporting bone that hold your teeth in place. Gum disease is the main cause of gum recession.
- Ineffective oral hygiene: Inadequate removal of dental bacterial plaque.
- Excessive brushing (and flossing): Brushing your teeth too hard, or for too long can damage the gum causing it to retract or wear away.
- Muscle attachments (frenums): pulling at the gum line.
- Habits: holding foreign objects between the teeth, such as nails that press on the gum tissues.
- Appliances: badly fitting removable partial dentures and orthodontic appliances (braces), tongue bolts, etc., can impinge upon gum tissues causing recession.
- Tobacco. Tobacco users are more likely to have sticky plaque on their teeth that is difficult to remove, which can cause gum recession.
- Body piercing of the lip or tongue Jewellery can rub the gums and irritate them to the point that gum tissue is worn away.
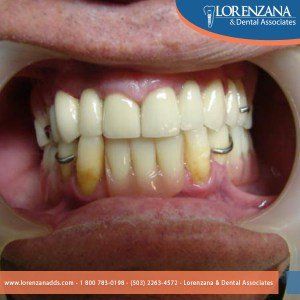
Treatment: Once the gingival recession origin is found, the next thing to do is proceed to the treatment.
- Professional Cleaning: During the deep cleaning, also called tooth scaling and root planning, plaque and tartar that has built up on the teeth and root surfaces below the gum line is carefully removed and the exposed root area is smoothed to make it more difficult for bacteria to attach itself.
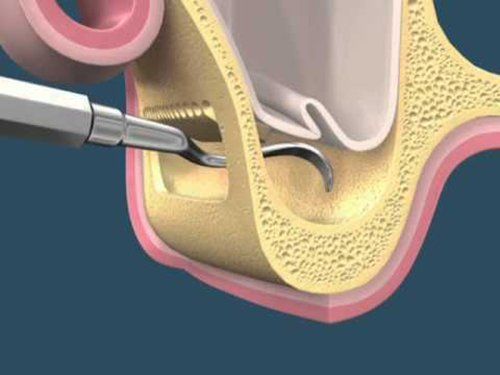
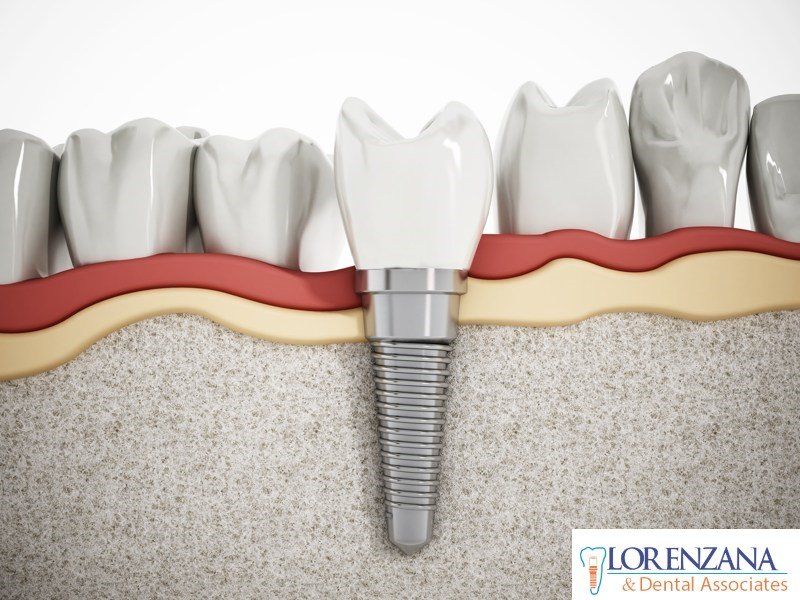
- Gum Surgery: For more serious cases a periodontal specialist/periodontist typically performs cosmetic or aesthetic surgery, or a general dentist who has taken advanced training in plastic periodontal surgical techniques.
- Gingival tissue grafting: Grafting techniques have been devised both to create and augment zones of attached gingival (gum) tissue where none exists, and to cover exposed root surfaces.
Prevention: The best way to prevent gum recession is to take good care of your mouth.
- Brush and floss your teeth every day in the proper way
- See your dentist and hygienist as recommended. If you have receding gums, the dentist or hygienist may want to see you more often.
- Always use a soft-bristled toothbrush
- Quit smoking if you smoke.
- Eat a well-balanced and healthy diet.
Acerca de la recesión gingival (encías retraídas)

Cuando ocurre una recesión de las encías, aparecen "bolsas", o brechas, que se forman entre los dientes y la línea de las encías, lo que facilita la acumulación de bacterias que causan enfermedades. Si no se trata, el tejido de soporte y las estructuras óseas de los dientes pueden dañarse severamente y, en última instancia, provocar la pérdida de un diente.
- Enfermedades periodontales: son infecciones bacterianas de las encías que destruyen el tejido de las encías y el hueso de soporte que mantiene sus dientes en su lugar. La enfermedad de las encías es la principal causa de la recesión de las encías.
- Higiene bucal ineficaz: eliminación inadecuada de la placa bacteriana dental.
- Cepillado excesivo (y uso de hilo dental): cepillarse los dientes demasiado fuerte o durante demasiado tiempo puede dañar la encía y hacer que se retraiga o desgaste.
- Inserciones musculares (frenums): tirando de la línea de las encías.
- Hábitos: sostener objetos extraños entre los dientes, como las uñas que presionan los tejidos de las encías.
- Electrodomésticos: prótesis parciales removibles mal ajustadas y aparatos de ortodoncia (aparatos ortopédicos), pernos de la lengua, etc., pueden afectar a los tejidos de las encías causando recesión.
- Tabaco. Los consumidores de tabaco tienen más probabilidades de tener una placa adhesiva en sus dientes que es difícil de eliminar, lo que puede causar una recesión de las encías.
- Perforación corporal del labio o la lengua La joyería puede frotar las encías e irritarlas hasta el punto de que el tejido de las encías se desgasta.

Tratamiento:
una vez que se encuentra el origen de la recesión gingival, el siguiente paso es proceder con el tratamiento.
- Limpieza profesional: durante la limpieza profunda, también llamada sarro dental y planificación de raíces, la placa y el sarro acumulados en los dientes y las raíces debajo de la línea de las encías se eliminan cuidadosamente y el área de la raíz expuesta se alisa para que sea más difícil para las bacterias para adjuntarse
- Cirugía de encías: para los casos más graves, un especialista / periodoncista periodontal normalmente realiza cirugías cosméticas o estéticas, o un dentista general que ha recibido capacitación avanzada en técnicas quirúrgicas periodontales plásticas.
- Injerto de tejido gingival: las técnicas de injerto se han diseñado tanto para crear como para aumentar las zonas de tejido gingival (encía) adherido donde no existe, y para cubrir las superficies de la raíz expuestas.
Prevención: la mejor manera de prevenir la recesión de las encías es cuidar bien de su boca.
- Cepíllese y use hilo dental todos los días de la manera adecuada
- Consulte a su dentista e higienista según las recomendaciones. Si tiene encías retraídas, es posible que el dentista o higienista desee verlo con más frecuencia.
- Utilice siempre un cepillo de cerdas suaves
- Deje de fumar si fuma.
Coma una dieta balanceada y saludable.