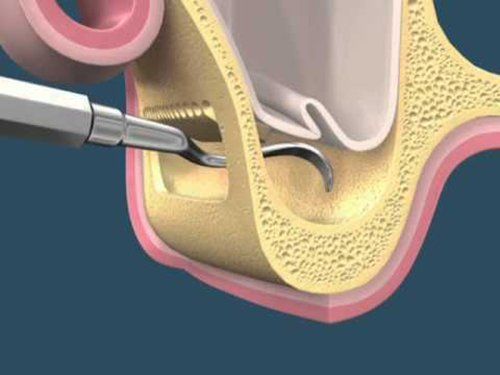
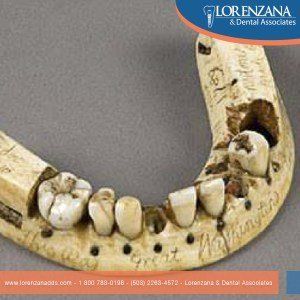
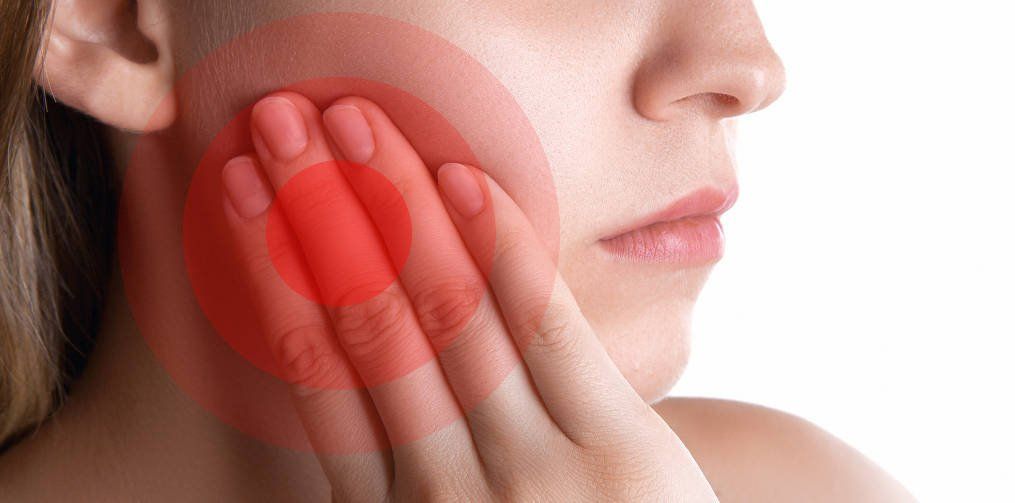
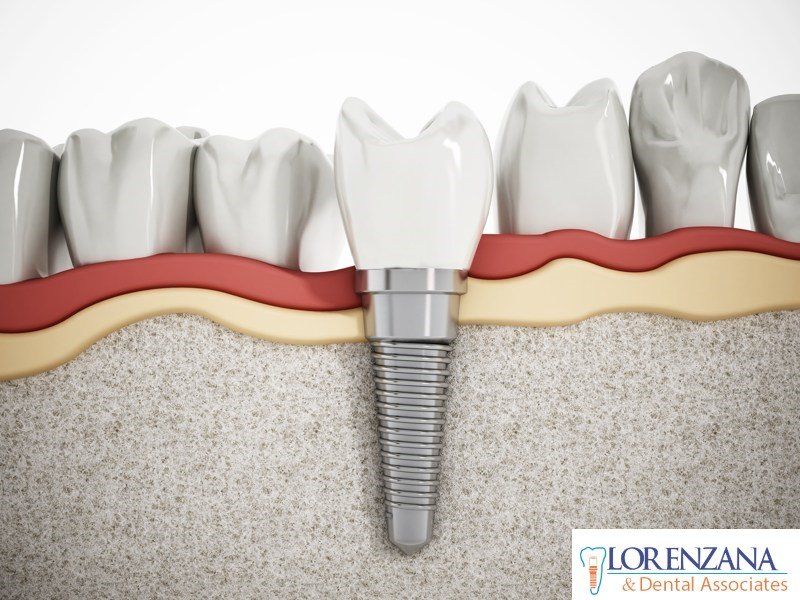
Bruxism: Symptoms Prevention & Treatment

Bruxism is clenching or grinding your teeth, often without being aware that your are doing it. In the United States, bruxism affects an estimated 30 to 40 million children and adults.
Some people grind their teeth only during sleep; this condition is called "nocturnal bruxism" or "sleep-related bruxism." Others grind their teeth during the daytime as well, most often during situations that make them feel tense or anxious. People with severe bruxism can fracture dental fillings or cause other types of tooth damage. Severe bruxism has also been blamed for some cases of temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD), mysterious morning headaches and unexplained facial pain.
Bruxism can have a variety of psychological and physical causes. In many cases, it has been linked to stress, but it can also simply be the body's reaction to the teeth being aligned wrong or a poor bite (the way the teeth come together). Bruxism can sometimes occur as a complication of severe brain injury, or a symptom of certain rare neuromuscular diseases involving the face. Bruxism also can be an uncommon side effect of some psychiatric medications, including antidepressant medications, including fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil).
Symptoms
Symptoms of bruxism include:
- Rhythmic contractions of the jaw muscles
- A grinding sound at night, which may disturb the sleep of someone who shares a bedroom with a "bruxer"
- A dull morning headache
- Jaw muscles that are tight or painful, especially in the morning
- Chronic facial pain
- Damaged teeth, fractured dental fillings and injured gums
Diagnosis
Your dentist will ask about your current life stresses, your general dental health and your daily medications. He or she also will want to know whether you routinely drink beverages containing alcohol or caffeine, because both of these chemicals seem to increase the tendency to grind your teeth.
If you share your bedroom, the dentist also may want to ask that person about your sleep habits, especially about any unusual grinding sounds heard during the night.
Your dentist will examine you, paying special attention to your mouth and jaw. During this exam, your dentist will check for tenderness in your jaw muscles, as well as for any obvious dental abnormalities, such as broken teeth, missing teeth or poor tooth alignment. If your dentist suspects that you have bruxism that is related to dental problems, he or she may conduct a more detailed assessment. In addition to checking your "bite," the dentist will examine your teeth and gums for damage caused by bruxism. The dentist will also take a series of mouth X-rays.
If your child grinds or clenches his or her teeth, discuss the problem with your family dentist. Although many children eventually outgrow bruxism, even short-term tooth grinding can cause damage to your child's permanent teeth.
Expected Duration
Of all children who brux between the ages of 3 and 10, more than half will stop spontaneously by age 13.
In teenagers and adults, how long bruxism lasts depends on its cause. For example, bruxism can last for many years if it is related to a stressful life situation that doesn't go away. However, if bruxism is being caused by a dental problem, it should stop when the teeth are repaired and realigned — often within a few dental visits.
Prevention
If your bruxism is related to stress, you may be able to prevent the problem by seeking professional counseling or by using strategies to help you learn to relax. Also, try cutting down on stimulants such as tobacco and caffeine.
In both children and adults, tooth damage related to bruxism can be prevented by wearing a night bite plate or a bite splint (a dental appliance worn at night to stop teeth grinding).
Treatment
The treatment of bruxism varies depending on its cause:
- Stress — If you have bruxism that is stress-related, your dentist or physician may recommend professional counseling, psychotherapy, biofeedback exercises or other strategies to help you relax. Your dentist or physician also may prescribe muscle relaxant medications to temporarily ease the spasm in your clenched and overworked jaw. If conventional therapy does not help, your dentist may refer you to an oral surgeon who may inject botulinum toxin directly into your jaw muscles (to temporarily interfere with muscle contractions).
- Dental problems — If your bruxism is related to tooth problems, your dentist will probably treat it with occlusal therapy (to correct tooth alignment). In severe cases, your dentist may need to use onlays or crowns to entirely reshape the biting surfaces of your teeth.
- Brain injury or neuromuscular illness — Your bruxism may be especially hard to treat if you have these medical problems. Your oral surgeon may give you injections of botulinum toxin if more conservative treatments fail.
- Medication — If you develop bruxism as a side effect of antidepressant medications, your doctor either can switch you to a different drug or give you another medication to counteract your bruxism.
When To Call A Professional
Call your physician or dentist if you have symptoms of bruxism, or if you are told that you grind your teeth while you sleep.
Also, make a dental appointment immediately if you fracture a tooth, lose a filling, or notice that your teeth are becoming abnormally loose in their sockets.
Prognosis
Even without special treatment, more than half of young children with bruxism stop grinding their teeth by age 13. Until your child stops bruxing on his or her own, your dentist can fit your child with a night bite plate to prevent excessive tooth wear. This device is effective in almost all children who use it as directed.
In teenagers and adults, the outlook is excellent if bruxism is treated properly. Even if all other therapies fail, injections of botulinum toxin can temporarily stop bruxism in most patients.
Source: colgate.com
Bruxismo: Sintomas Prevención y Tratamiento

Bruxismo es apretar o rechinar los dientes, a menudo sin estar consientes que lo hacemos. En los Estados Unidos, el bruxismo afecta alrededor de 30 a 40 millones de niños y adultos.
Algunas personas rechinan sus dientes solamente mientras duermen, esta condición se conoce como bruxismo nocturno o bruxismo relacionado al sueño. Otras personas rechinan sus dientes también durante el día, más que todo en situaciones que les hacen sentir tensis o ansiosos. Personas con bruxismo severo pueden llegar a fracturar rellenos dentales o causar otra clase de daños. El bruxismo severo también se ha determinado como la causa de algunos casos de trastornos de la articulación temporomandibular (ATM), casos de misteriosos dolores de cabeza matutinos y dolor facial inexplicable.
El bruxismo puede tener una variedad de causas físicas y psicologicas. En muchos casos se asocia al estrés, pero puede simplemente ser la reacción del cuerpo a una mala alineación dental o una mordida pobre (la forma en que los dientes se juntan). El bruxismo puede surgir como una complicación de daño cerebral severo, o un sintoma a ciertas enfermedades neuromusculares raras afectan a la cara. El bruxismo puede incluso ser un efecto secundario de algunos medicamentos psiquiátricos, incluyendo medicamentos antidepresivos, incluyendo fluoxetina (Prozac), sertralina (Zoloft) y paroxetina (Paxil).
- Contracciones ritmicas en los musculos de las mandíbulas
- Sonido de rechinamiento por las noches, el cual pudiera interrumpir el sueño de quienes comparten habitación con un "bruxador"
- Matutino dolor de cabeza sordo
- Musculos de la mandíbula contraidos o con dolor, especialmente por la mañana
- Dolor facial crónico
- Dientes dañados, rellenos fracturados y encías dañadas
Diagnóstico
- Su dentista le preguntará sobre el estrés actual en su vida, su salud dental general y sobre sus medicamentos diarios. El o ella querrá saber también si en su rutina se incluyen bebidas que contienen alcohol o cafeína, porque ambos parecer incrementar la tendencia a rechinar los dientes.
- Si comparte el cuarto con alguien, el dentista podría querer preguntarle a esa persona sobre sus hábitos de sueño, especialmente sobre algún sonido inusual de rechinamiento por las noches.
- Su dentista le examinará, poniendo especial atención a su boca y mandíbula, durante este examen el dentista revisará si existe alguna tensión en los musculos de la mandíbula, al igual que obvias anormalidades dentales, tales como dientes fracturados, dientes faltantes o una pobre alineación dental.
- Si su dentista sospecha que usted padece bruxismo el cual está relacionado a problemas dentales, el o ella podría proceder con una evaluación más detallada. Adicionalmente a revisar su mordida, el dentista examinará sus dientes y encías en busca de daños causados por bruxismo. El dentista también tomará una serie de radiografías de su boca.
Duración esperada
De todos los niños que bruxan en las edades entre 3 y 10 años, más de la mitad se detendrá expontaneamente al llegar a los 13 años de edad.
En adolescentes y adultos, el tiempo que dure el bruxismo depende de las causas que este tenga. Por ejemplo, el bruxismo puede durar muchos años si está relacionado a una situación estresante en la vida que no se va. De cualquier manera si el bruxismo es causado por un problema dental, este debería detenerse cuando los dientes sean restaurados o realineados - por lo regular con unas cuantas visitas al dentista.
Prevención
Si su bruxismo está relacionado al estrés, usted podría prevenir el problema buscando asistencia profesional o usando estrategias que le ayuden a aprender a relajarse. También trate de redicur el consumo de estimulantes como el tabaco y el café.
En ambos casos, niños y adultos, el daño dental causado por bruxismo puede prevenirse usando por las noches una férula de descarga o una guarda occlusal.
Tratamiento
El tratamiento de bruxismo varía dependiendo de las causas:
- Estrés: Si usted padece bruxismo relacionado al estrés, su dentista o médico podría recomendarle asistencia profesional, fisioterapia, ejercicios de relajaciónu otras estrategias que le ayuden a relajarse. Su dentista o médico también podría prescribirle relajantes musculares para temporalmente reducir los espasmos en mandíbula contraida y sobrecargada. Si la terapia convencional no ayuda, su dentista le referirá a un cirujano oral quien le inyectará toxina botulínica directo en los músculos de su mandíbula (para interferir temporalmente con las contracciones en su mandíbula).
- Problemas dentales: Si su bruxismo está relacionado a problemas dentales, su dentista probablemente tratará el problema con terapia oclusal (corrección de alineación). En casos severos su dentista podría necesitar utilizar incrustaciones de porcelana o coronas para rehacer completamente la forma de mordida de los dientes.
- Lesión cerebral o enfermedades neuromusculares: Este bruxismo podría ser especialmente dificil de tratar. Su cirujano oral podría aplicarle inyecciones de toxina botulínica si tratamientos más conservadores fallan.
- Medicamentos: Si usted desarrolla bruxismo como efecto secundario de medicamentos antidepresivos, su doctor podría cambiar el medicamento por otro o prescribirle uno adicional para contrarestar el bruxismo.
Cuándo llamar a un profesional
Llame a su médico o dentista si tiene síntomas de bruxismo, o si le dicen que rechina los dientes mientras duerme.
También, haga una cita con el dentista inmediatamente si se fractura un diente, pierde un empaste o nota que sus dientes se están volviendo anormalmente sueltos en sus órbitas.
Prognosis
Incluso sin un tratamiento especial, más de la mitad de los niños pequeños con bruxismo dejan de rechinar los dientes antes de los 13 años. Hasta que el niño deje de masticar por su cuenta, su dentista puede placa de mordida nocturna para evitar el desgaste excesivo de los dientes. Este dispositivo es efectivo en casi todos los niños que lo usan según las indicaciones.
En adolescentes y adultos, el pronóstico es excelente si el bruxismo se trata adecuadamente. Incluso si todas las demás terapias fracasan, las inyecciones de toxina botulínica pueden detener temporalmente el bruxismo en la mayoría de los pacientes.
Fuente: colgate.com